
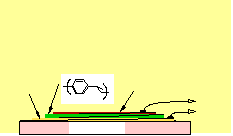
Construction
of Polymer LEDs

Energy (eV)
3.5
2.5
1.5
Absorbance
PPV
Photoluminescence
15 K
T=77 K
Polymer LEDs
cathode
Friend,
Burroughes and Tatsuya, Physics World
(Vol. 12) p35-40
(1999)
O
O
S
n
n
PPV
n
2.7 eV
5.2 eV
PSS
PEDOT
4.8 eV
5.0 eV
2.8 eV
SO
3
H
semiconducting
polymer
1
00 nm
calcium
indium-tin-
oxide anode
40 nm
The calcium
injects electrons into
the polymer
film, while the anode
injects
holes. When an electron and
hole capture one
another within the
PPV, they form
neutral "excitons"
(bound excited
states) that decay
by emitting a
photon of light.

Poor
interchain p
overlap
enhances
photo- and
electro- luminescence
Side chain
structure reduces side chain
crystallization
and frustrates packing
Poly(2-methoxy-5-(2'-ethylhexoxy)-phenylene)
LED design
strategy
poly(
p
n
-phenylene
vinylene)
Nature, 347, 539
(1990),
US patent
5,247,190
Burroughes et
al.,
indium tin
oxide
glass substrate
aluminum,
magnesium,
or
low-workfunction
metal
External
Circuit

Major applications: LEDs

Electron and
hole mobilities are now an issue